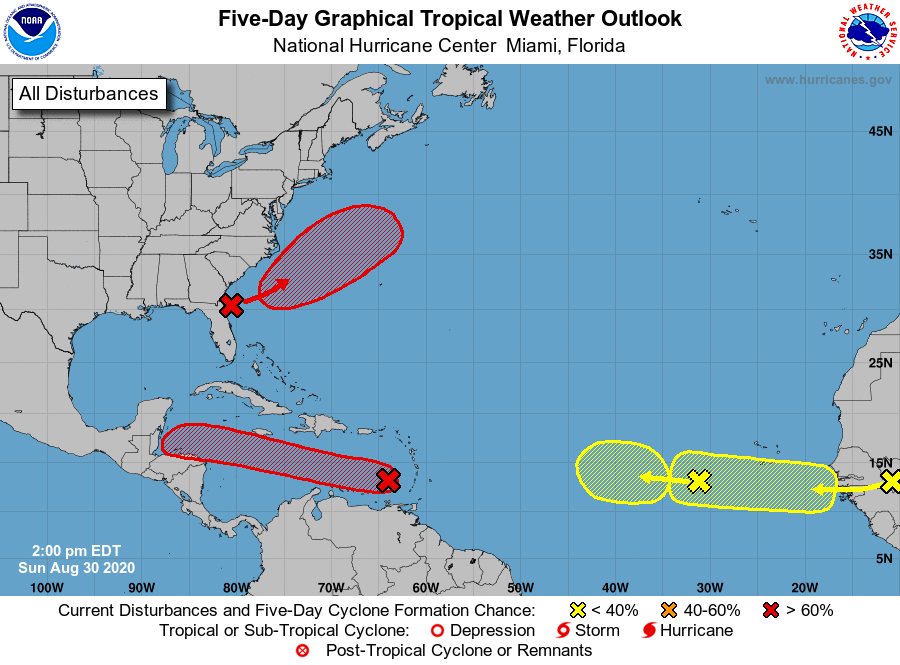
NHC: Formation chances increase for two tropical waves
August 30, 2020
LSP: Pedestrian struck and killed in single-vehicle crash
August 31, 2020A 57-year-old man in Calcasieu Parish died from a head injury after falling from a roof. Another resident in Calcasieu Parish died from carbon monoxide poisoning; LDH will provide additional details as it verifies them.
LDH now has verified 8 Hurricane Laura-related deaths due to carbon monoxide poisoning—representing more than half of the total Laura-related deaths to date.
Below are details on the 14 deaths LDH has verified to date:
- 14-year-old female, Vernon Parish, fallen tree
- 51-year-old male, Jackson Parish, fallen tree
- 68-year-old male, Acadia Parish, fallen tree
- 64-year-old female, Allen Parish, fallen tree
- Male, Calcasieu Parish, drowning
- 24-year-old male, Calcasieu Parish, carbon monoxide poisoning from generator
- 56-year-old female, Calcasieu Parish, carbon monoxide poisoning from generator
- 61-year-old male, Calcasieu Parish, carbon monoxide poisoning from generator
- 81-year-old female, Calcasieu Parish, carbon monoxide poisoning from generator
- 72-year-old male, Calcasieu Parish, carbon monoxide poisoning from generator
- 84-year-old male, Allen Parish, carbon monoxide poisoning from generator
- 80-year-old female, Allen Parish, carbon monoxide poisoning from generator
- 57-year-old male, Calcasieu Parish, head injury after falling from roof
- One resident, Calcasieu Parish, carbon monoxide poisoning
Opening windows or doors or using fans will not prevent the build-up of carbon monoxide. If you start to feel sick, dizzy or weak while using a generator, get to fresh air immediately.
Generators should be placed outside, more than 20 feet away from the home, doors, windows and vents that could allow carbon monoxide to come indoors.
The generator should be kept dry and should not be used in wet conditions.






